How a brick and mortar retailer has competed successfully against online rivals by implementing a customer centric omni channel strategy.
“Customers today expect a level of convenience that brick and mortar retailers do not meet easily”
THE CHALLENGE:
 Target has been one of the largest US large format brick and mortar retailers present in every state with thousands of brick and mortar stores since the early 20th century, initially struggling to keep up with competition of Amazon. Like many other retailers, Target had a hard time keeping pace with Amazon’s home delivery service and the convenience of the Amazon Prime Pantry functionality, that allowed customers to shop for groceries online with Amazon conveniently, quickly, and getting their orders delivered within 2 hour for free. Customers stopped shopping in stores because shopping in stores meant spending at least 2-3 hours on a weekly basis with a repetitive task that people did not enjoy and preferred to spend that time with their families, friends and not in a store shopping every Saturday.
Target has been one of the largest US large format brick and mortar retailers present in every state with thousands of brick and mortar stores since the early 20th century, initially struggling to keep up with competition of Amazon. Like many other retailers, Target had a hard time keeping pace with Amazon’s home delivery service and the convenience of the Amazon Prime Pantry functionality, that allowed customers to shop for groceries online with Amazon conveniently, quickly, and getting their orders delivered within 2 hour for free. Customers stopped shopping in stores because shopping in stores meant spending at least 2-3 hours on a weekly basis with a repetitive task that people did not enjoy and preferred to spend that time with their families, friends and not in a store shopping every Saturday.

THE SOLUTION:
Target, like many of its peers (K-Mart, Rainbow Foods, Cub Foods), started struggling competing against online competitors such as Amazon. A radical change had to be implemented quickly to avoid going bankrupt.
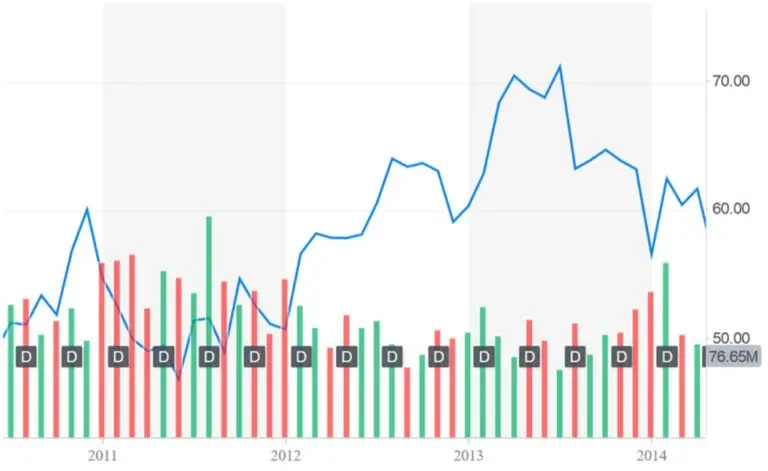
In 2014, the company has faced multiple challenges: an aggressive over expansion in Canada has strained the company’s financial resources while a highly publicized data security breach has also created negative impact for the retailer’s online business. As a result both CIO and CEO resigned and new leadership has taken over the company.
To tackle financial challenges and aggressive online competition, Target has initiated a bold and radical series of steps to change its business model to be fully immersed in an omni channel engagement with its customers.
As a result, Target’s revenues have increased, contributing to Target being named retailer of the year in 2018 and over performing both expected revenue and target profit figures. Current stock prices reflect well on Target’s performance, especially when comparing the prices to its peers.
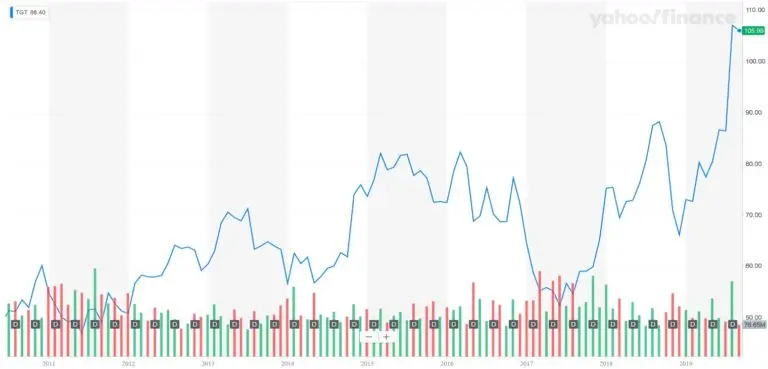
What exactly has Target done to implement a seamlessly omni channel strategy that has allowed it to compete so effectively against online competitors such as Amazon? Multiple initiatives all focused on the customer.
Radical change in its stores: Target has chosen to implement a radical change in its stores by essentially converting them into a fulfillment center and a showroom style shopping experience. By doing this Target has gained a warehouse network more extensive than its online competitors, allowing it to fulfill orders quickly and efficiently. By performing this change, Target gained the capacity and ability to fulfill customer demand on multiple channels seamlessly and quickly (home deliver in 2 hours or less, like Amazon, in addition to in-store options as described below), which in turn brought a level of convenience to its customers unparalleled even among online retailers.
Online orders home delivered: Relying on its extensive network of fulfillment centers, Target gained the ability to fulfill and deliver to customers’ homes online orders quickly and efficiently, allowing the retailer to compete with online competitors effectively.
Online orders picked up in store: Customers not only have the choice of ordering online and getting the order delivered to their homes but can also pick the online order up in a store. This is a great choice to people on the road and driving by the store, allowing them to immediately or in very short time pick their order up. The warehouse in the store picks the online order just the same way as home delivery but places the completed pick for pickup. Process does not involve additional complexity but allowed Target to offer something to its customers online retailers never could, effectively out competing its online rivals with a differentiated service.
In store shopping delivered to the car: Customers also have the ability to shop in the store and scan, using their mobile phone or a scanner provided in the store, each item they wish to purchase but not actually carry the scanned items to the cash register. When ready to leave, the shopper checks out on the handheld device and goods purchased are ready to be picked up by car. For the store, the process is not more complex than picking an online order for car pickup, yet for the customer Target offers a new service for convenience not available at its online rivals. Families choose this convenient option to avoid lines at the cash registers but still be able to see and touch and try what they buy, saving time and the effort of pushing a cart through the store.
Traditional in store shopping: Customers still have the ability to shop like they used to: go through the store with a shopping cart, collect goods for purchase and check out at an automated or traditional cash register. Target is opening smaller stores closer to urban centers to reach traditional customers better.

To help customers, Target has also made available real time product availability information for its customers. Target’s website and mobile interface both allow customers to check real-time availability of searched products at stores within a defined range of distance from the customers’ location. Target has also added a cartwheel app designed to make omni channel shopping and communicating with the customer easier by providing a convenient access to weekly ads, coupons, discounts and updates.
CONCLUSION:
By applying innovative ideas and processes supported by technology to deliver on new engagement channels to customers, Target has effectively out-competed its online rivals and has come to dominate the retail space in its markets in its own segment successfully.
To implement such an omni channel customer focused strategy Target had to make radical changes quickly, however the initiatives paid off and have proven that brick and mortar retailers can compete effectively against online competitors, to the degree that online competition has felt the loss of advantage on the online side of retailing and has begun investing in brick and mortar stores (Amazon bought Whole Foods).
SOURCES:
1. https://finance.yahoo.com/chart/TGT
2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Target_Corporation
3. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Target_Corporation
4. https://www.target.com/
5. https://corporate.target.com/about
6. https://www.inc.com/jason-aten/targets-small-format-stores-are-its-biggest-weapon-against-amazon-walmart.html
7. https://www.cnbc.com/2019/08/23/target-opens-100-mini-stores-remodels-500-bigger-ones.html
8. https://www.cnbc.com/2019/08/25/disney-and-target-are-teaming-up-to-open-stores-with-each-others-help.html
9. https://www.retaildive.com/news/retailer-of-the-year-target/541905/
10. https://www.insider-trends.com/a-store-in-every-state-inside-targets-retail-strategy/








